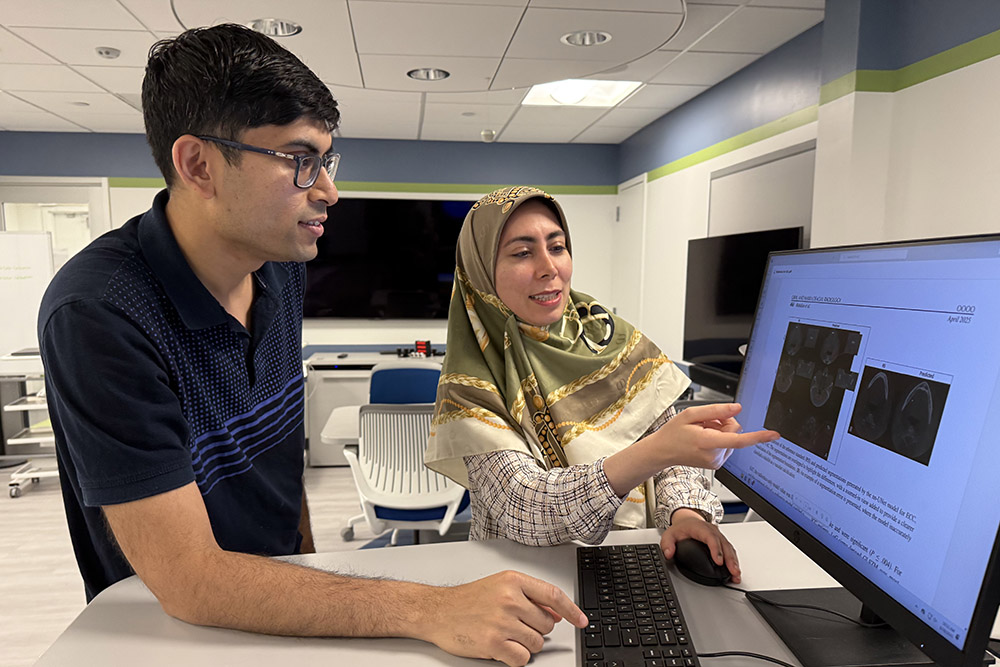
Collaboration with the University at Buffalo will Democratize Access to Artificial Intelligence and Research Computing
The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) has awarded a $13.77 million grant to Stony Brook University’s Institute for Advanced Computational Science (IACS), in collaboration with the University at Buffalo. The award, “Sustainable Cyber-infrastructure for Expanding Participation,” will deliver cutting-edge computing and data resources to power advanced research nationwide.
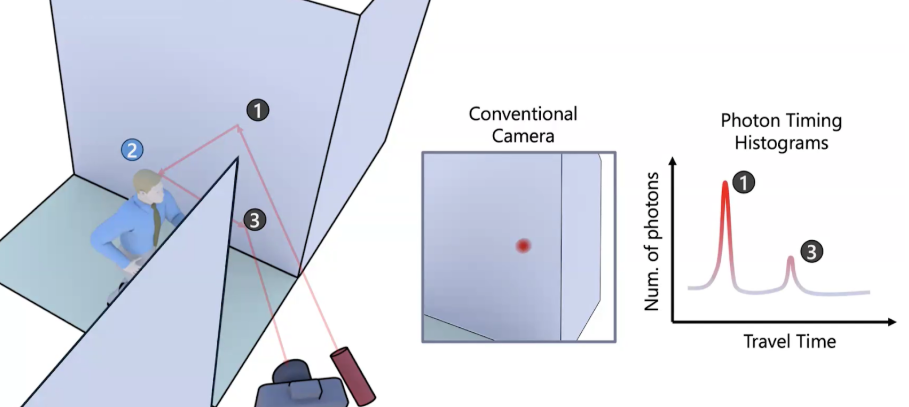
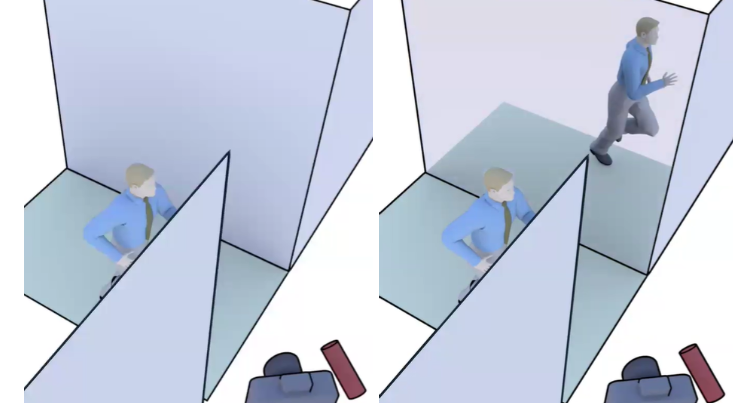
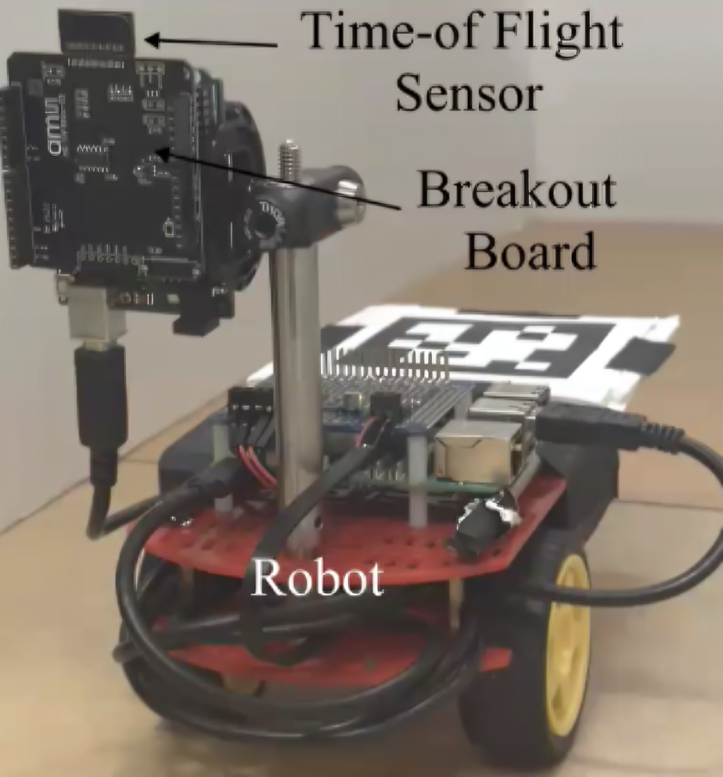
SBU researchers train robots to detect hidden hazards around corners using single-photon LiDAR. Their project is the first to implement this navigation technology using commercially available, lightweight sensors.

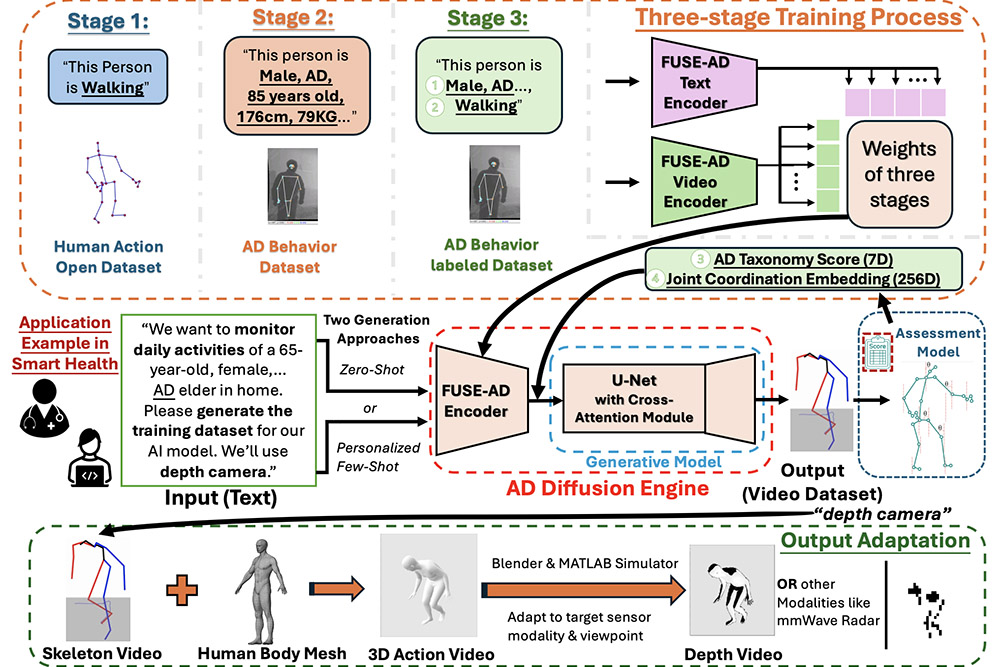
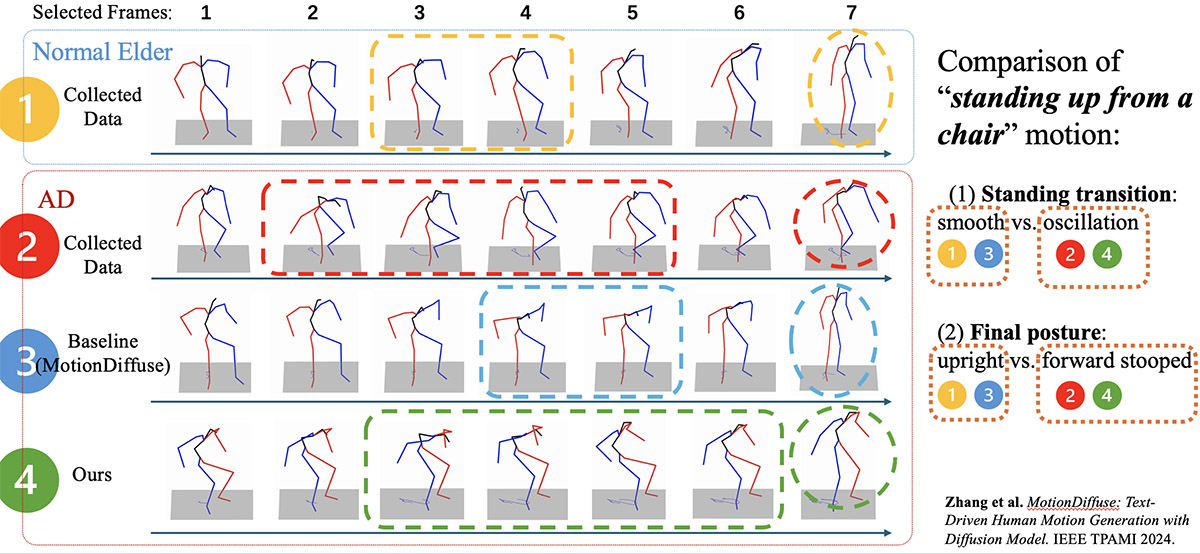
Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most urgent public health challenges for aging Americans. Nearly seven million Americans over the age of 65 are currently living with the disease, and that number is projected to nearly double by 2060, according to the Alzheimer’s Association.
Computer Science Professors Stanley Bak and Scott Smolka to develop AI-powered solutions for preventing aviation incidents.
New York-based Stony Brook University (SBU) has bought a new high-performance computing (HPC) cluster online, NVwulf. Described as “sister system” to the university’s existing SeaWulf cluster, Stony Brook said NVwulf marks a “significant upgrade” in campus-wide computational capabilities.
A machine-learning algorithm spotted signs of “covert consciousness” in coma patients—in some cases, days before doctors could do so.